Workshop 2
Exercise solutions
library(tidyverse)
#> ── Attaching core tidyverse packages ──── tidyverse 2.0.0 ──
#> ✔ dplyr 1.1.4 ✔ readr 2.1.4
#> ✔ forcats 1.0.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.1
#> ✔ ggplot2 3.5.0 ✔ tibble 3.2.1
#> ✔ lubridate 1.9.3 ✔ tidyr 1.3.0
#> ✔ purrr 1.0.2
#> ── Conflicts ────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
#> ✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
#> ✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
#> ℹ Use the conflicted package (<http://conflicted.r-lib.org/>) to force all conflicts to become errorsPart I
Exercise 1
Task: Write and Use a Function Objective: Create a function that calculates the cube of a number and use this function to calculate the cube of 3.
Hint: Use the structure of the square_function as a template.
Exercise 2
Task: Analyze a Numeric Vector Objective: Write a function named summarize_vector that takes a numeric vector as input and calculates the median, variance, and creates a boxplot. The function should print the median and variance, and return them as a list. Use the airquality$Ozone data for analysis.
Hint: Similar to analyze_vector, check if the input is numeric and use median, var, and boxplot functions.
summarize_vector <- function(x, plot_title = "Boxplot") {
if (!is.numeric(x)) {
stop("Input must be a numeric vector")
}
median_value <- median(x, na.rm = TRUE)
variance_value <- var(x, na.rm = TRUE)
cat("Median:", median_value, "\n")
cat("Variance:", variance_value, "\n")
boxplot(x, main = plot_title, xlab = "Values", col = "coral", border = "darkred")
return(list(median = median_value, variance = variance_value))
}
# Example usage with the airquality$Ozone vector
result <- summarize_vector(airquality$Ozone, "Ozone Levels Boxplot")
#> Median: 31.5
#> Variance: 1088.201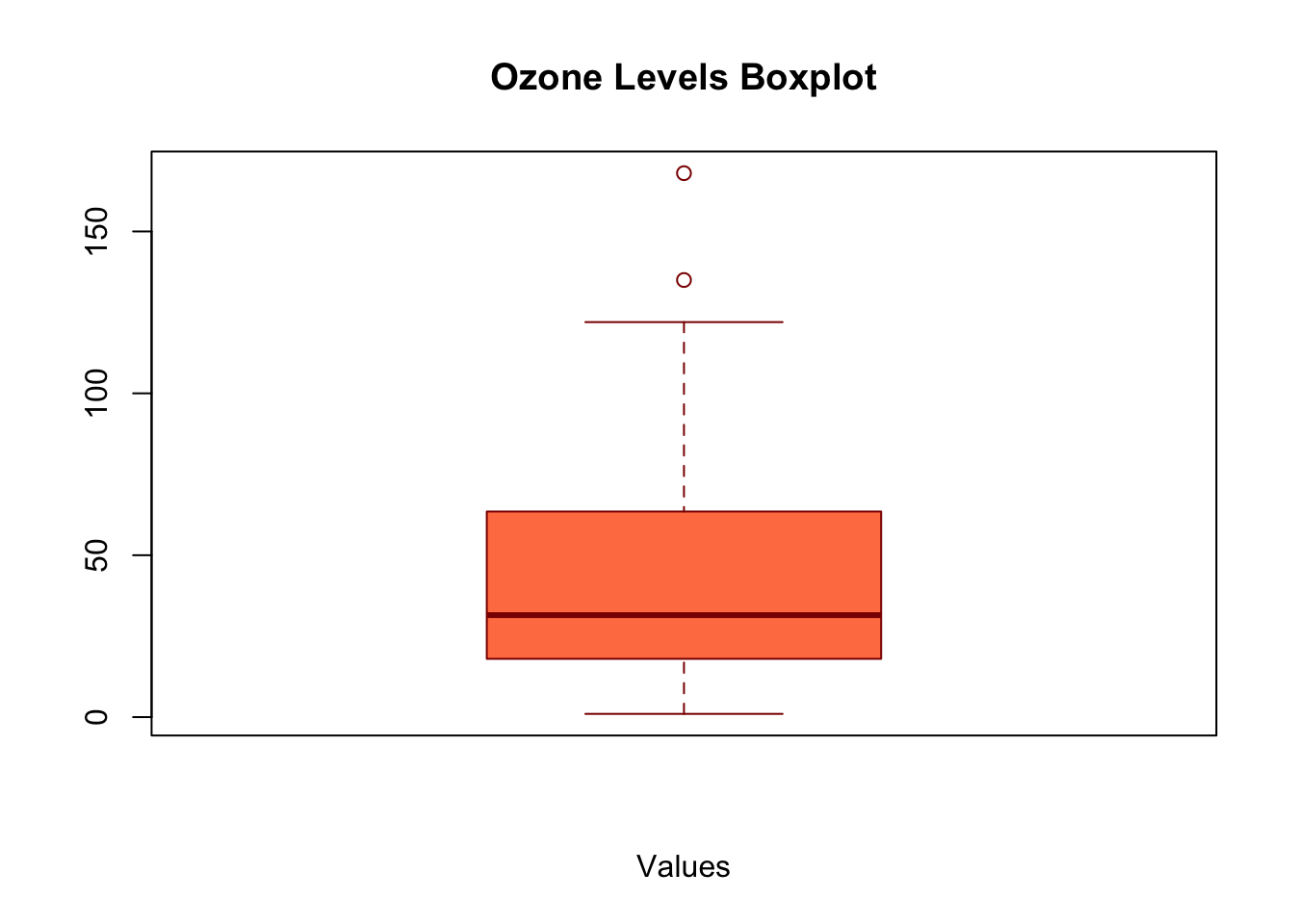
Exercise 3
Task: Using if Statements Objective: Create an R script that checks if a number is negative, zero, or positive and prints an appropriate message. Test your script with the number -4.
Hint: Use an if statement followed by else if and else.
Exercise 4
Task: For Loop Objective: Write a function using a for loop that calculates the sum of squares of numbers from 1 to n. Use this function to calculate the sum of squares for n=10.
Hint: Iterate from 1 to n, and keep adding the square of each number to a result variable.
Part II
Exercise 1
- Load the data Parade2005.txt.
- Determine the mean earnings in California.
- Determine the number of individuals residing in Idaho.
- Determine the mean and the median earnings of celebrities.
Parade2005 <- read.table(file = '/Users/dilancaro/Library/Mobile Documents/com~apple~CloudDocs/Workshops/John Jay/R Workshop/R-workshop-John-Jay/John Jay Workshop Data/Parade2005.txt')
head(Parade2005)
#> earnings age gender state celebrity
#> 1 10000 26 male ND no
#> 2 10000000 18 female CA yes
#> 3 85000 39 male NE no
#> 4 75000 50 female NC no
#> 5 91500 61 male DE no
#> 6 49500 39 female SD no
Parade2005 %>% filter(state == "CA") %>%
summarize(mean = mean(earnings))
#> mean
#> 1 6241430
Parade2005 %>% group_by(state == "CA") %>%
summarize(mean = mean(earnings))
#> # A tibble: 2 × 2
#> `state == "CA"` mean
#> <lgl> <dbl>
#> 1 FALSE 1108577.
#> 2 TRUE 6241430
Parade2005 %>%
group_by(celebrity) %>%
summarize(mean = mean(earnings), median = median(earnings))
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> celebrity mean median
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 no 61038. 49500
#> 2 yes 17107273. 19000000
Parade2005 %>%
group_by(celebrity) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = celebrity, y = earnings)) + theme_bw() +
geom_boxplot(color = "blue")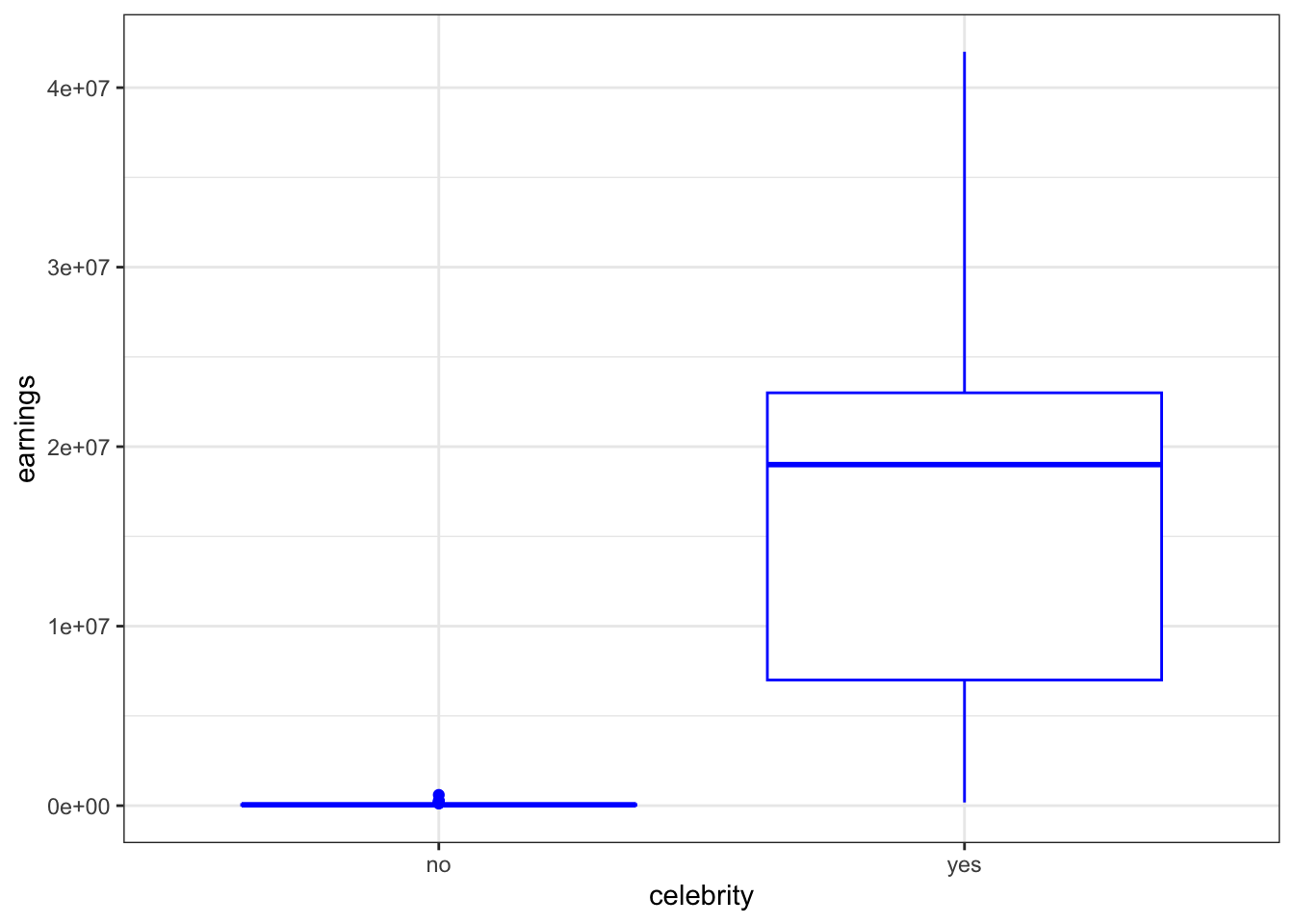
boxplot(earnings~ celebrity , data= Parade2005)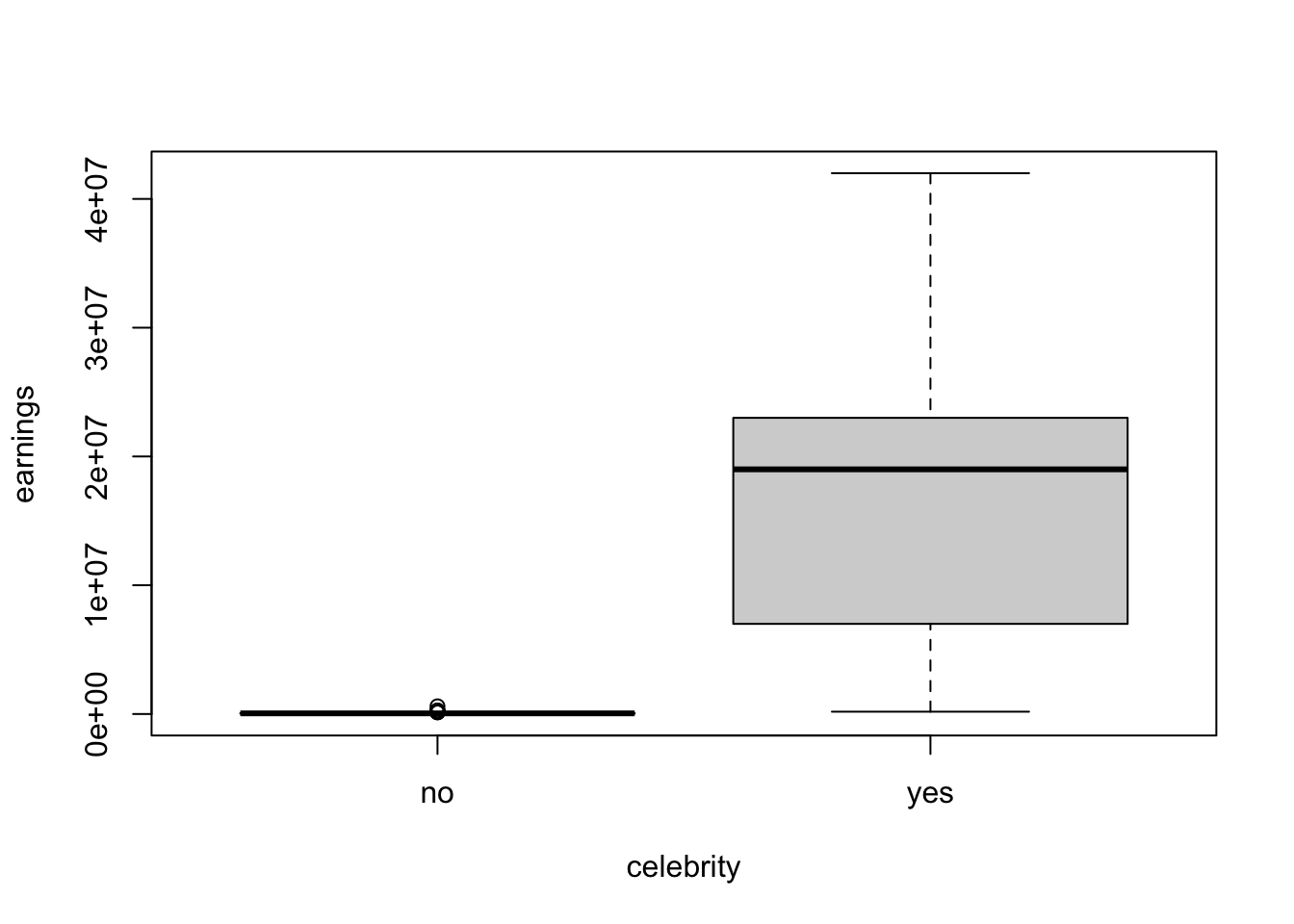
Exercise 2
Use the skills you obtained in Part I.
- Inspect the top rows of the data set.
- How many observations does the data set contain?
- Calculate the total exposure (exposition) in each region (type_territoire).
policy_data <- read.csv(file = '/Users/dilancaro/Library/Mobile Documents/com~apple~CloudDocs/Workshops/John Jay/R Workshop/R-workshop-John-Jay/John Jay Workshop Data/PolicyData.csv', sep = ';')
head(policy_data)
#> numeropol debut_pol fin_pol freq_paiement langue
#> 1 3 14/09/1995 24/04/1996 mensuel F
#> 2 3 25/04/1996 23/12/1996 mensuel F
#> 3 6 1/03/1995 27/02/1996 annuel A
#> 4 6 1/03/1996 14/01/1997 annuel A
#> 5 6 15/01/1997 31/01/1997 annuel A
#> 6 6 1/02/1997 28/02/1997 annuel A
#> type_prof alimentation type_territoire
#> 1 Technicien V\xe9g\xe9tarien Urbain
#> 2 Technicien V\xe9g\xe9tarien Urbain
#> 3 Technicien Carnivore Urbain
#> 4 Technicien Carnivore Urbain
#> 5 Technicien Carnivore Urbain
#> 6 Technicien Carnivore Urbain
#> utilisation presence_alarme marque_voiture sexe
#> 1 Travail-quotidien non VOLKSWAGEN F
#> 2 Travail-quotidien non VOLKSWAGEN F
#> 3 Travail-occasionnel oui NISSAN M
#> 4 Travail-occasionnel oui NISSAN M
#> 5 Travail-occasionnel oui NISSAN M
#> 6 Travail-occasionnel oui NISSAN M
#> cout1 cout2 cout3 cout4 nbsin exposition cout age
#> 1 NA NA NA NA 0 0.61095890 NA 29
#> 2 NA NA NA NA 0 0.66301370 NA 30
#> 3 279.5839 NA NA NA 1 0.99452055 279.58 42
#> 4 NA NA NA NA 0 0.87397260 NA 43
#> 5 NA NA NA NA 0 0.04383562 NA 44
#> 6 NA NA NA NA 0 0.07397260 NA 44
#> duree_permis annee_vehicule
#> 1 10 1989
#> 2 11 1989
#> 3 21 1994
#> 4 22 1994
#> 5 23 1994
#> 6 23 1994
nrow(policy_data)
#> [1] 39075Exercise 3
Use the skills obtained in Part I:
- Inspect the top rows of the data.
- Select the data for countries in Asia.
- Which type of variable is
country?
library(gapminder)
head(gapminder)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 6
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.
#> 2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.
#> 3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.
#> 4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836.
#> 5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740.
#> 6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786.
asia <- filter(gapminder, continent == "Asia")
class(gapminder$country)
#> [1] "factor"Exercise 4
The variable country in the gapminder data set is a factor variable.
- What are the possible levels for country in the subset asia.
- Is this the result you expected?
library(gapminder)
gapminder
#> # A tibble: 1,704 × 6
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.
#> 2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.
#> 3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.
#> 4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836.
#> 5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740.
#> 6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786.
#> 7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.9 12881816 978.
#> 8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.8 13867957 852.
#> 9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.7 16317921 649.
#> 10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.8 22227415 635.
#> # ℹ 1,694 more rows
# Subset data for Asian countries
asia <- subset(gapminder, continent == "Asia")
levels(asia$country)
#> [1] "Afghanistan" "Albania"
#> [3] "Algeria" "Angola"
#> [5] "Argentina" "Australia"
#> [7] "Austria" "Bahrain"
#> [9] "Bangladesh" "Belgium"
#> [11] "Benin" "Bolivia"
#> [13] "Bosnia and Herzegovina" "Botswana"
#> [15] "Brazil" "Bulgaria"
#> [17] "Burkina Faso" "Burundi"
#> [19] "Cambodia" "Cameroon"
#> [21] "Canada" "Central African Republic"
#> [23] "Chad" "Chile"
#> [25] "China" "Colombia"
#> [27] "Comoros" "Congo, Dem. Rep."
#> [29] "Congo, Rep." "Costa Rica"
#> [31] "Cote d'Ivoire" "Croatia"
#> [33] "Cuba" "Czech Republic"
#> [35] "Denmark" "Djibouti"
#> [37] "Dominican Republic" "Ecuador"
#> [39] "Egypt" "El Salvador"
#> [41] "Equatorial Guinea" "Eritrea"
#> [43] "Ethiopia" "Finland"
#> [45] "France" "Gabon"
#> [47] "Gambia" "Germany"
#> [49] "Ghana" "Greece"
#> [51] "Guatemala" "Guinea"
#> [53] "Guinea-Bissau" "Haiti"
#> [55] "Honduras" "Hong Kong, China"
#> [57] "Hungary" "Iceland"
#> [59] "India" "Indonesia"
#> [61] "Iran" "Iraq"
#> [63] "Ireland" "Israel"
#> [65] "Italy" "Jamaica"
#> [67] "Japan" "Jordan"
#> [69] "Kenya" "Korea, Dem. Rep."
#> [71] "Korea, Rep." "Kuwait"
#> [73] "Lebanon" "Lesotho"
#> [75] "Liberia" "Libya"
#> [77] "Madagascar" "Malawi"
#> [79] "Malaysia" "Mali"
#> [81] "Mauritania" "Mauritius"
#> [83] "Mexico" "Mongolia"
#> [85] "Montenegro" "Morocco"
#> [87] "Mozambique" "Myanmar"
#> [89] "Namibia" "Nepal"
#> [91] "Netherlands" "New Zealand"
#> [93] "Nicaragua" "Niger"
#> [95] "Nigeria" "Norway"
#> [97] "Oman" "Pakistan"
#> [99] "Panama" "Paraguay"
#> [101] "Peru" "Philippines"
#> [103] "Poland" "Portugal"
#> [105] "Puerto Rico" "Reunion"
#> [107] "Romania" "Rwanda"
#> [109] "Sao Tome and Principe" "Saudi Arabia"
#> [111] "Senegal" "Serbia"
#> [113] "Sierra Leone" "Singapore"
#> [115] "Slovak Republic" "Slovenia"
#> [117] "Somalia" "South Africa"
#> [119] "Spain" "Sri Lanka"
#> [121] "Sudan" "Swaziland"
#> [123] "Sweden" "Switzerland"
#> [125] "Syria" "Taiwan"
#> [127] "Tanzania" "Thailand"
#> [129] "Togo" "Trinidad and Tobago"
#> [131] "Tunisia" "Turkey"
#> [133] "Uganda" "United Kingdom"
#> [135] "United States" "Uruguay"
#> [137] "Venezuela" "Vietnam"
#> [139] "West Bank and Gaza" "Yemen, Rep."
#> [141] "Zambia" "Zimbabwe"
#alternative
library(dplyr)
asia <- gapminder %>%
filter(continent == "Asia")
levels(asia$country)
#> [1] "Afghanistan" "Albania"
#> [3] "Algeria" "Angola"
#> [5] "Argentina" "Australia"
#> [7] "Austria" "Bahrain"
#> [9] "Bangladesh" "Belgium"
#> [11] "Benin" "Bolivia"
#> [13] "Bosnia and Herzegovina" "Botswana"
#> [15] "Brazil" "Bulgaria"
#> [17] "Burkina Faso" "Burundi"
#> [19] "Cambodia" "Cameroon"
#> [21] "Canada" "Central African Republic"
#> [23] "Chad" "Chile"
#> [25] "China" "Colombia"
#> [27] "Comoros" "Congo, Dem. Rep."
#> [29] "Congo, Rep." "Costa Rica"
#> [31] "Cote d'Ivoire" "Croatia"
#> [33] "Cuba" "Czech Republic"
#> [35] "Denmark" "Djibouti"
#> [37] "Dominican Republic" "Ecuador"
#> [39] "Egypt" "El Salvador"
#> [41] "Equatorial Guinea" "Eritrea"
#> [43] "Ethiopia" "Finland"
#> [45] "France" "Gabon"
#> [47] "Gambia" "Germany"
#> [49] "Ghana" "Greece"
#> [51] "Guatemala" "Guinea"
#> [53] "Guinea-Bissau" "Haiti"
#> [55] "Honduras" "Hong Kong, China"
#> [57] "Hungary" "Iceland"
#> [59] "India" "Indonesia"
#> [61] "Iran" "Iraq"
#> [63] "Ireland" "Israel"
#> [65] "Italy" "Jamaica"
#> [67] "Japan" "Jordan"
#> [69] "Kenya" "Korea, Dem. Rep."
#> [71] "Korea, Rep." "Kuwait"
#> [73] "Lebanon" "Lesotho"
#> [75] "Liberia" "Libya"
#> [77] "Madagascar" "Malawi"
#> [79] "Malaysia" "Mali"
#> [81] "Mauritania" "Mauritius"
#> [83] "Mexico" "Mongolia"
#> [85] "Montenegro" "Morocco"
#> [87] "Mozambique" "Myanmar"
#> [89] "Namibia" "Nepal"
#> [91] "Netherlands" "New Zealand"
#> [93] "Nicaragua" "Niger"
#> [95] "Nigeria" "Norway"
#> [97] "Oman" "Pakistan"
#> [99] "Panama" "Paraguay"
#> [101] "Peru" "Philippines"
#> [103] "Poland" "Portugal"
#> [105] "Puerto Rico" "Reunion"
#> [107] "Romania" "Rwanda"
#> [109] "Sao Tome and Principe" "Saudi Arabia"
#> [111] "Senegal" "Serbia"
#> [113] "Sierra Leone" "Singapore"
#> [115] "Slovak Republic" "Slovenia"
#> [117] "Somalia" "South Africa"
#> [119] "Spain" "Sri Lanka"
#> [121] "Sudan" "Swaziland"
#> [123] "Sweden" "Switzerland"
#> [125] "Syria" "Taiwan"
#> [127] "Tanzania" "Thailand"
#> [129] "Togo" "Trinidad and Tobago"
#> [131] "Tunisia" "Turkey"
#> [133] "Uganda" "United Kingdom"
#> [135] "United States" "Uruguay"
#> [137] "Venezuela" "Vietnam"
#> [139] "West Bank and Gaza" "Yemen, Rep."
#> [141] "Zambia" "Zimbabwe"asia$country allows the same outcomes as gapminder$country. This includes many countries outside of Asia.
In some cases, even after filtering a dataset, the factor levels of the subset might still include all levels present in the original dataset. This is because subsetting the rows does not automatically drop unused factor levels. To see only the levels that are present in the subset, you might need to use droplevels():
asia$country <- droplevels(asia$country)
levels(asia$country)
#> [1] "Afghanistan" "Bahrain"
#> [3] "Bangladesh" "Cambodia"
#> [5] "China" "Hong Kong, China"
#> [7] "India" "Indonesia"
#> [9] "Iran" "Iraq"
#> [11] "Israel" "Japan"
#> [13] "Jordan" "Korea, Dem. Rep."
#> [15] "Korea, Rep." "Kuwait"
#> [17] "Lebanon" "Malaysia"
#> [19] "Mongolia" "Myanmar"
#> [21] "Nepal" "Oman"
#> [23] "Pakistan" "Philippines"
#> [25] "Saudi Arabia" "Singapore"
#> [27] "Sri Lanka" "Syria"
#> [29] "Taiwan" "Thailand"
#> [31] "Vietnam" "West Bank and Gaza"
#> [33] "Yemen, Rep."Exercise 5
Bin the life expectancy in 2007 in a factor variable. 1. Select the observations for year 2007. 2. Bin the life expectancy in four bins of roughly equal size (hint: quantile). 3. How many observations are there in each bin?
gapminder2007 <- filter(gapminder, year == 2007)
breaks <- c(0, quantile(gapminder2007$lifeExp, c(0.25, 0.5, 0.75)), Inf)
breaks
#> 25% 50% 75%
#> 0.00000 57.16025 71.93550 76.41325 Inf
gapminder2007 <- gapminder2007 %>%
mutate(life_expectancy_binned = cut(gapminder2007$lifeExp, breaks))
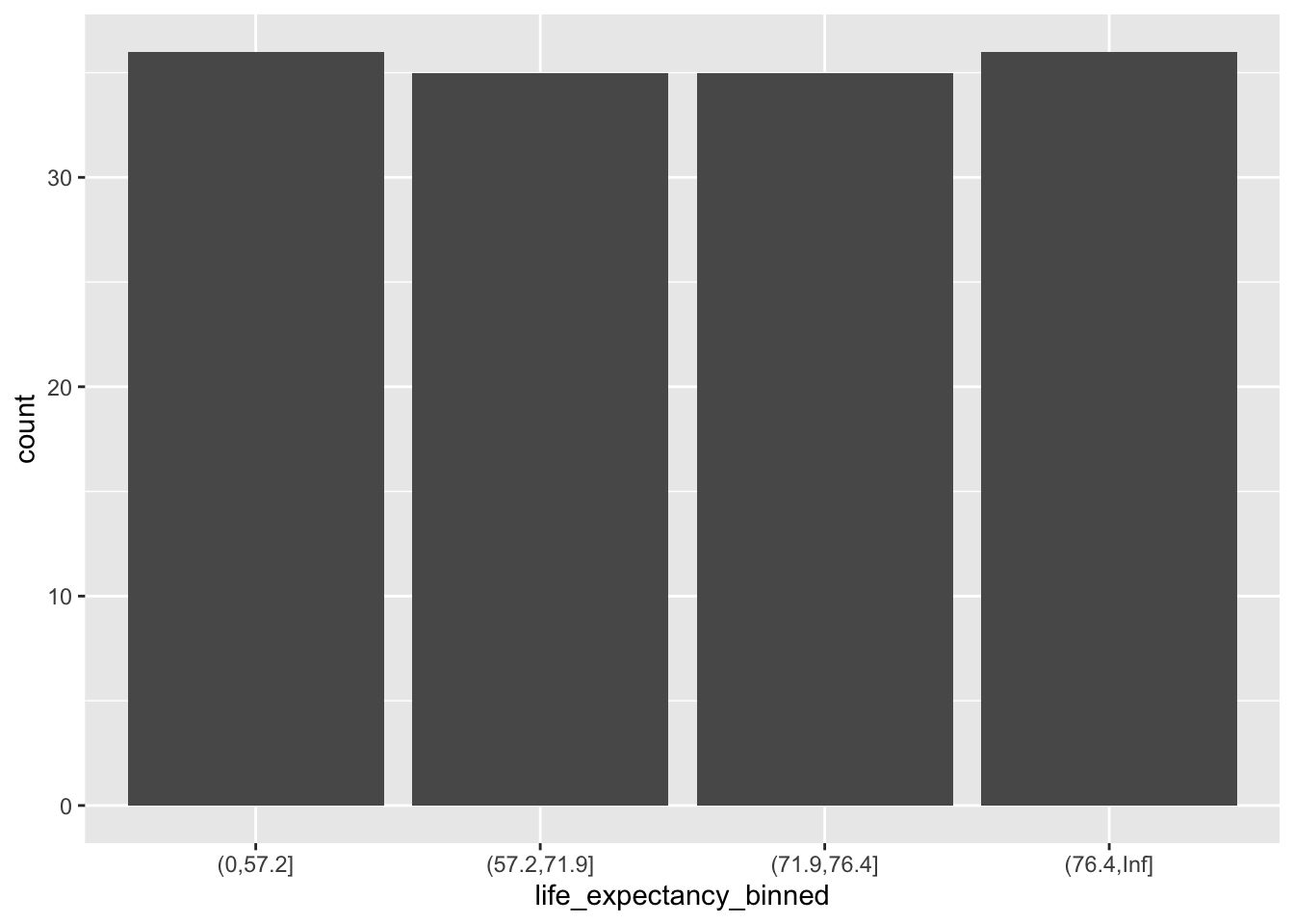
gapminder2007 %>%
group_by(life_expectancy_binned) %>%
summarise(frequency = n())
#> # A tibble: 4 × 2
#> life_expectancy_binned frequency
#> <fct> <int>
#> 1 (0,57.2] 36
#> 2 (57.2,71.9] 35
#> 3 (71.9,76.4] 35
#> 4 (76.4,Inf] 36
gapminder2007
#> # A tibble: 142 × 7
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 2007 43.8 31889923 975.
#> 2 Albania Europe 2007 76.4 3600523 5937.
#> 3 Algeria Africa 2007 72.3 33333216 6223.
#> 4 Angola Africa 2007 42.7 12420476 4797.
#> 5 Argentina Americas 2007 75.3 40301927 12779.
#> 6 Australia Oceania 2007 81.2 20434176 34435.
#> 7 Austria Europe 2007 79.8 8199783 36126.
#> 8 Bahrain Asia 2007 75.6 708573 29796.
#> 9 Bangladesh Asia 2007 64.1 150448339 1391.
#> 10 Belgium Europe 2007 79.4 10392226 33693.
#> # ℹ 132 more rows
#> # ℹ 1 more variable: life_expectancy_binned <fct>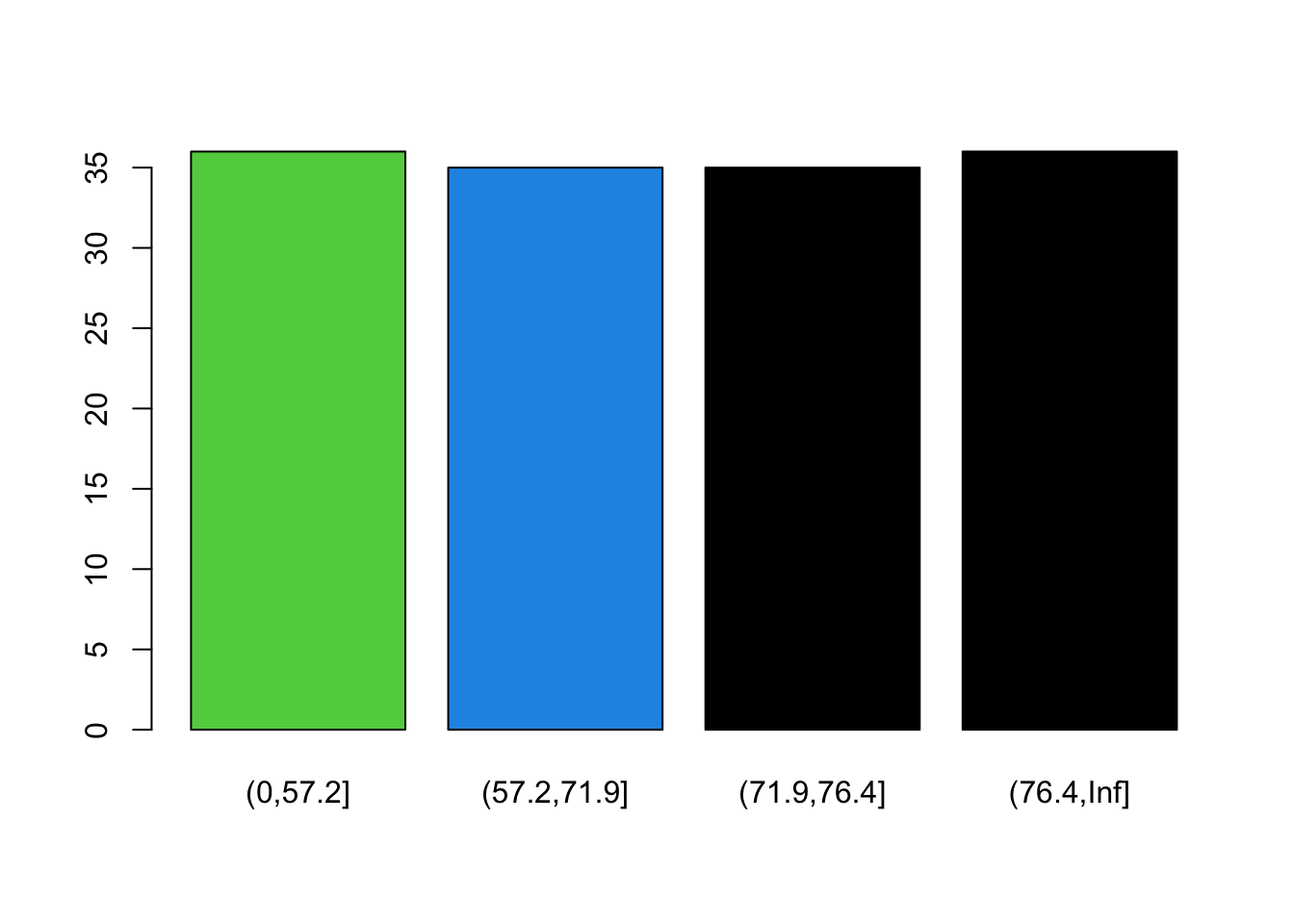
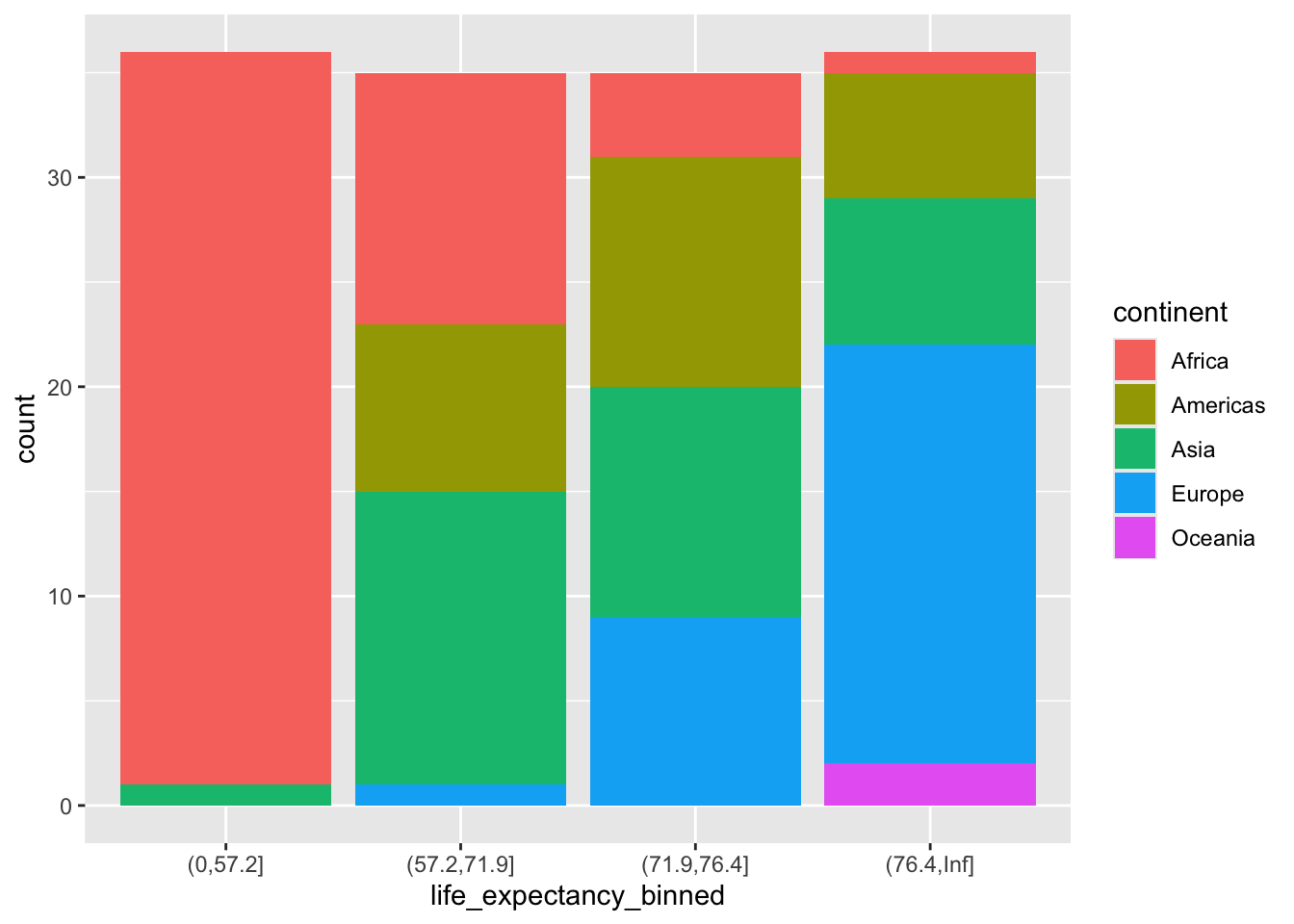
ggplot(gapminder2007) +
geom_bar(aes(life_expectancy_binned,
fill = continent),
position = position_dodge())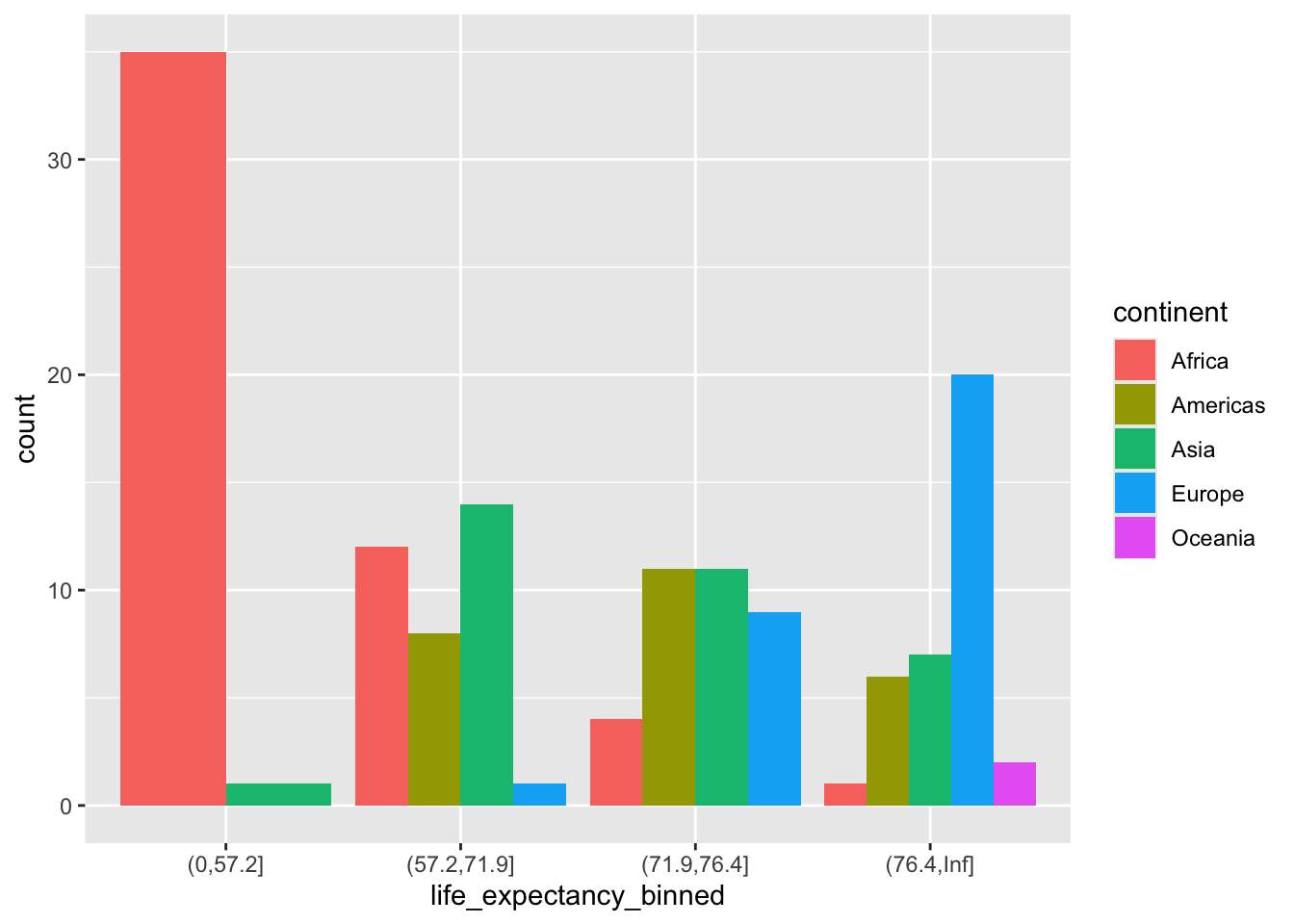
ggplot(gapminder2007) +
geom_bar(aes(life_expectancy_binned,
fill = continent,
y = after_stat(prop), group = continent),
position = position_dodge())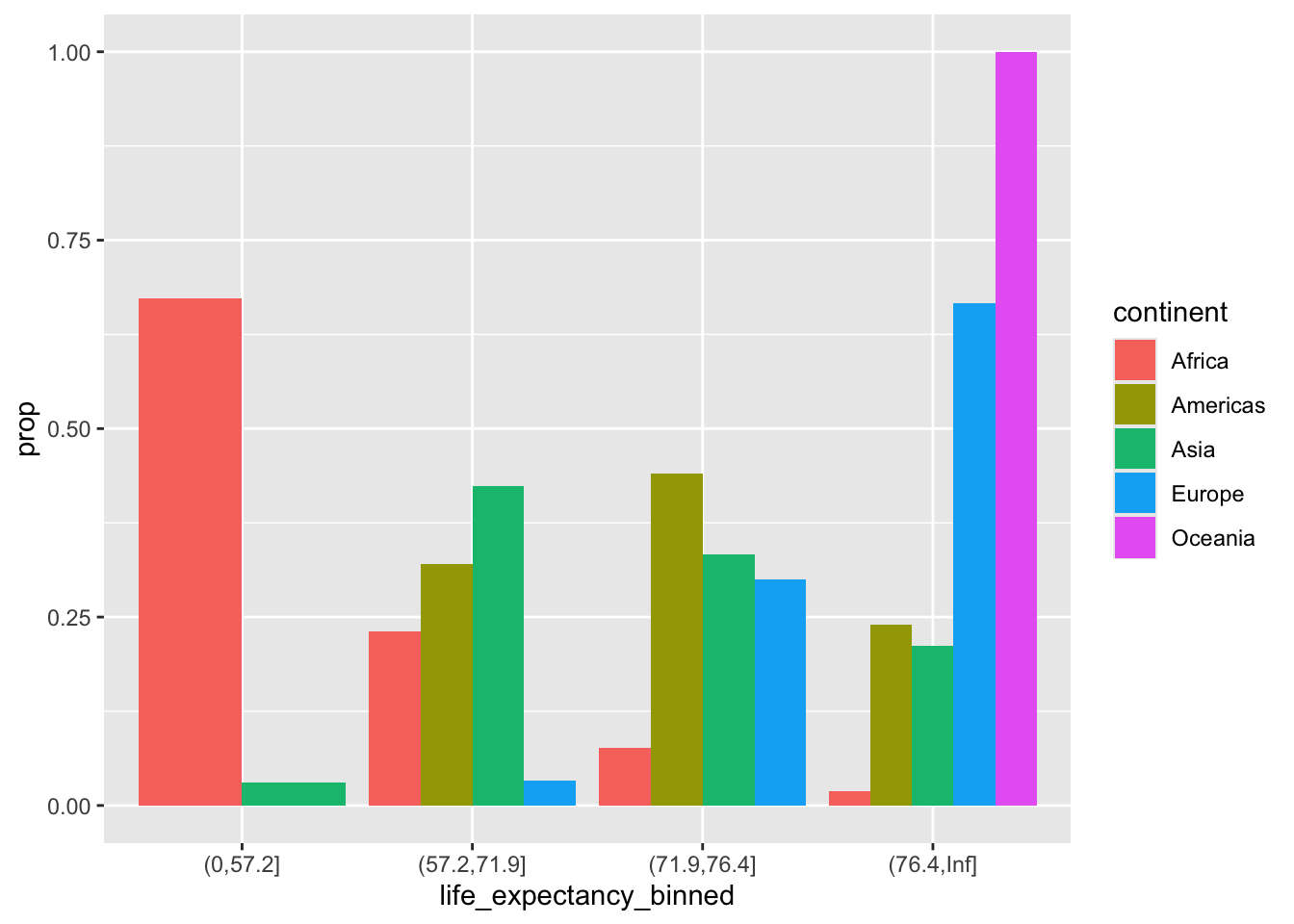
y = ..prop.. and group = continent plot the proportion within each group instead of the absolute count.
Exercise 1: Explore Missingness
Dataset: ChickWeight
Task: Determine if the ChickWeight dataset contains any missing values. Print a message stating whether the dataset has missing values or not.
Hint Use the any() function combined with is.na() applied to the dataset.
How to use any()
Exercise 2: Calculate Summary Statistics Before Handling NA
Dataset: mtcars
Task: The mtcars dataset is almost complete but let’s pretend some values are missing in the mpg (miles per gallon) column. First, artificially introduce missing values into the mpg column (e.g., set the first three values of mpg to NA). Then, calculate and print the mean and standard deviation of mpg without removing or imputing the missing values.
Hint: Modify the mtcars$mpg directly to introduce NAs. Use mean() and sd() functions with na.rm = FALSE to calculate statistics without handling NA.
# Artificially introduce missing values into the mpg column of mtcars
mtcars$mpg[1:3] <- NA
# Calculate and print the mean and standard deviation without removing NA
mean_mpg <- mean(mtcars$mpg, na.rm = FALSE)
sd_mpg <- sd(mtcars$mpg, na.rm = FALSE)
print(paste("Mean of mpg without handling NA:", mean_mpg))
#> [1] "Mean of mpg without handling NA: NA"
print(paste("Standard deviation of mpg without handling NA:", sd_mpg))
#> [1] "Standard deviation of mpg without handling NA: NA"Exercise 3: Impute Missing Values with Column Median
Dataset: mtcars with modified mpg
Task: First Calculate the mean and standard deviation handling the missing values.
Then,Impute the artificially introduced missing values in the mpg column with the column’s median (excluding the missing values). Print the first 6 rows of the modified mtcars dataset.
Now, calculate the mean and standard deviation with the imputed values.
Hint: First, calculate the median of mpg excluding NAs. Then, use indexing to replace NAs with this median.
mean_mpg <- mean(mtcars$mpg, na.rm = TRUE)
sd_mpg <- sd(mtcars$mpg, na.rm = TRUE)
print(paste("Mean of mpg handling NA:", mean_mpg))
#> [1] "Mean of mpg handling NA: 19.9344827586207"
print(paste("Standard deviation of mpg handling NA:", sd_mpg))
#> [1] "Standard deviation of mpg handling NA: 6.31422859568932"
# Calculate the median of mpg excluding NAs
median_mpg <- median(mtcars$mpg, na.rm = TRUE)
median_mpg
#> [1] 18.7
# Impute the missing values with the median
mtcars$mpg[is.na(mtcars$mpg)] <- median_mpg
# Print the first 6 rows of the modified mtcars dataset
head(mtcars)
#> mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am
#> Mazda RX4 18.7 6 160 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1
#> Mazda RX4 Wag 18.7 6 160 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1
#> Datsun 710 18.7 4 108 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1
#> Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0
#> Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0
#> Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1 0
#> gear carb
#> Mazda RX4 4 4
#> Mazda RX4 Wag 4 4
#> Datsun 710 4 1
#> Hornet 4 Drive 3 1
#> Hornet Sportabout 3 2
#> Valiant 3 1
##
mean_mpg <- mean(mtcars$mpg)
sd_mpg <- sd(mtcars$mpg)
print(paste("Mean of mpg imputed NA:", mean_mpg))
#> [1] "Mean of mpg imputed NA: 19.81875"
print(paste("Standard deviation of mpg imputed NA:", sd_mpg))
#> [1] "Standard deviation of mpg imputed NA: 6.01205442316491"Exercise 4: Identifying Complete Rows
Dataset: Airquality
Task: Before any analysis, you want to ensure that only complete cases are used. Create a new dataset from airquality that includes only the rows without any missing values. Print the number of rows in the original versus the cleaned dataset.
Hint Use complete.cases() on the dataset and then subset it.
data("airquality")
# Create a new dataset from airquality that includes only rows without any missing values
complete_Airquality<- airquality[complete.cases(airquality), ]
# Print the number of rows in the original versus the cleaned dataset
print(paste("Original dataset rows:", nrow(airquality)))
#> [1] "Original dataset rows: 153"
print(paste("Cleaned dataset rows:", nrow(complete_Airquality)))
#> [1] "Cleaned dataset rows: 111"Exercise 5: Advanced Imputation on a Subset
Dataset: mtcars
Task: Create a subset of mtcars containing only the mpg, hp (horsepower), and wt (weight) columns. Introduce missing values in hp and wt columns (e.g., set first two values of each to NA). Perform multiple imputation using the mice package on this subset with 3 imputations, and extract the third completed dataset. Print the first 6 rows of this completed dataset.
Hint: Subset mtcars first, then modify to add NAs. Use mice() for imputation and complete() to extract the desired imputed dataset.
# Load the necessary package
library(mice)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'mice'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter
#> The following objects are masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> cbind, rbind
# Create a subset of mtcars
mtcars_subset <- mtcars[, c("mpg", "hp", "wt")]
# Introduce missing values
mtcars_subset$hp[1:2] <- NA
mtcars_subset$wt[1:2] <- NA
# Perform multiple imputation
imputed_data_subset <- mice(mtcars_subset, m=3, method='pmm', seed = 123)
#>
#> iter imp variable
#> 1 1 hp wt
#> 1 2 hp wt
#> 1 3 hp wt
#> 2 1 hp wt
#> 2 2 hp wt
#> 2 3 hp wt
#> 3 1 hp wt
#> 3 2 hp wt
#> 3 3 hp wt
#> 4 1 hp wt
#> 4 2 hp wt
#> 4 3 hp wt
#> 5 1 hp wt
#> 5 2 hp wt
#> 5 3 hp wt
# Extract the third completed dataset
completed_data_subset <- complete(imputed_data_subset, 3)
# Print the first 6 rows of the completed data
head(completed_data_subset)
#> mpg hp wt
#> Mazda RX4 18.7 175 3.440
#> Mazda RX4 Wag 18.7 109 3.440
#> Datsun 710 18.7 93 2.320
#> Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 110 3.215
#> Hornet Sportabout 18.7 175 3.440
#> Valiant 18.1 105 3.460
# Sample data for the lengths of bolts
bolt_lengths <- c(6, 7, 7.5, 5.1, 4.9, 5.2, 6.1, 6.5, 6.8, 7)
# Perform the Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test
# H0: median bolt length = 5 cm
# Ha: median bolt length != 5 cm
test_result <- wilcox.test(bolt_lengths, mu = 5, alternative = "two.sided", conf.int = TRUE)
#> Warning in wilcox.test.default(bolt_lengths, mu = 5,
#> alternative = "two.sided", : cannot compute exact p-value
#> with ties
#> Warning in wilcox.test.default(bolt_lengths, mu = 5,
#> alternative = "two.sided", : cannot compute exact
#> confidence interval with ties
# Output the results
print(test_result)
#>
#> Wilcoxon signed rank test with continuity correction
#>
#> data: bolt_lengths
#> V = 53.5, p-value = 0.009252
#> alternative hypothesis: true location is not equal to 5
#> 95 percent confidence interval:
#> 5.500024 6.999965
#> sample estimates:
#> (pseudo)median
#> 6.2
# Extract and print the p-value explicitly
cat("P-value:", test_result$p.value, "\n")
#> P-value: 0.009252446